No matter what label you identify with inside the content universe, the touchpoints identified in the service blueprint — and in fact, the entire service design process — are goldmines for those concerned with providing content that guides, instructs, and delights customers in need of services of any kind.
If you think of digital content as being integral to supporting digital experiences and marketing strategies, you would not be wrong. Content well done supports your audience (or user) journey through the marketing funnel, from discovery to conversion — and ultimately, retention — guiding the user down the proverbial happy path to obtaining goods or services, without friction, and maybe with a bit of enjoyment along the way.
Content that supports the successful purchase of goods being offered by a brand signal a win for both the business and the customer. Whether completing a transaction in a traditional physical location or on the brand’s app or website, everyone gets what they want when a coveted object or much-needed item is available for purchase and that purchase is made successfully.
But things at the ‘services’ end of ‘goods and services’ sometimes suffer for a lack of attention to detail, especially where content is concerned. Customers seeking services like paying bills or making an appointment not only expect that these types of transactions to be completed without a hitch, but they also expect:
- Ease of use
- A clear understanding of the service being offered
- Content that provides context or explains the options being presented
And there’s another piece to this type of transaction — whether in person, online, or on the phone — that sometimes gets overlooked, and that’s the importance of considering the experience of the brand’s service providers in the delivery of the service being offered. That means if you pay a bill online but that payment fails to post within the time stated on the site or app, a customer service representative should be able to locate your account, understand the steps you took to pay the bill, and provide you with helpful information about why your payment hasn’t been posted.
Similarly, if you visit a home improvement store and purchase an item that requires installation or some other kind of on-site work, but the installers or contractors fail to show up, a call to the store where the transaction was initiated and paid for (or in some cases, a call to third-party scheduling or dispatch services) should connect you with someone who not only has access to all the information about the service you paid for but also knows what to do when the workers you expected don’t show up.
With so much focus on digital experiences that foster the purchase of products or goods, sometimes the service piece gets neglected. The problem with that is, as more brand experiences blur the lines between products and services, especially in digital spaces, customers expect that they will receive services on par with the value of the goods they purchased.
And when they don’t? That same digital interaction — the purchase — that was initially so pleasant can make a customer salty, oftentimes in a very public way. We see you, social media, and we acknowledge the power of the customer takedown.
So what can a brand do to ensure that every touchpoint is positive, (relatively) free of friction, and keeps employees informed and customers loyal?
That’s where service design comes into the mix.
Service by definition
In seeking to better understand what service design is, it might be useful to first distinguish a product from a service.
In a virtual workshop titled Getting Started With Service Design, offered by Think Company, products and services are defined as follows:
- Products: Products are tangible; you interact with them. They can be physical or digital — a hammer, a sofa, a phone, an app.
- Services: You can’t hold a service and assess it in your hands. It’s a collection of touchpoints; a mixture of physical, digital, and human interactions all working together to bring value to a customer. A product is just one touchpoint within a service.
In the book ‘Service Design: From Insight to Implementation,’ authors Andy Polaine, Lavrans Løvlie, and Ben Reason write that service design shares its origin with other modern design disciplines that can be traced back to industrial design, a field that saw its rise in the 1920s.
The authors write, “What [first generation industrial designers] had in common was a drive to use new industrial technology to improve people’s standard of living…[they] strove to turn industrialization into a force for good.”
In more contemporary times, G. Lynn Shostack first (re)introduced the concept of service design — and more specifically, the differentiation between products and services — in a 1982 article titled How to Design a Service.
Shostack wrote, “The difference between products and services is more than semantic. Products are tangible objects that exist in both time and space; services consist solely of acts or process(es) and exist in time only. The basic distinction between “things” and “processes” is the starting point for a focused investigation of services. Services are rendered; products are possessed. Services cannot be possessed; they can only be experienced, created, or participated in.”
Now that we have a clear understanding of what differentiates a product from a service, let’s take a brief look at the roots of service design, how it is defined, and why it’s an important tool for service providers.
So then, what is service design?
This definition of service design comes from the Nielsen Norman Group:
- “Service design is the activity of planning and organizing a business’s resources (people, props, and processes) in order to (1) directly improve the employee’s experience, and (2) indirectly, the customer’s experience.”
Similarly, the Interaction Design Foundation defines service design this way:
- “Service design is a process where designers create sustainable solutions and optimal experiences for both customers in unique contexts and any service providers involved. Designers break services into sections and adapt fine-tuned solutions to suit all users’ needs in context—based on actors, location, and other factors.”
Design differentiation: what’s in a name
There are myriad design methodologies and frameworks that overlap with service design but are distinct in their approach to designing experiences. Let’s take a look at a few of the more popular approaches to better understand the relationship with service design.
Design thinking and service design
- “Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems, and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. ”
Though this process has firm roots in design, it is often used outside of creative teams to approach and solve problems.
Authors Polaine et al explain the distinction between service design and design thinking this way:
- “We see service design as distinct from design thinking in that it is also about doing design and implementation. It also makes use of designers’ abilities to visualize and make abstract ideas tangible.”
Human- (or user-) centered design and service design
Digital Product Manager Franki Lake offers this definition of human- or user-centered design:
“User-centered design is the overarching framework of processes [emphasis added] that integrate a broad set of practices around understanding the needs, wants, and limitations of end-users.”
By this definition, user-centered design is a framework, and service design is one of several methodologies within that framework that designers can use to create value for customers.
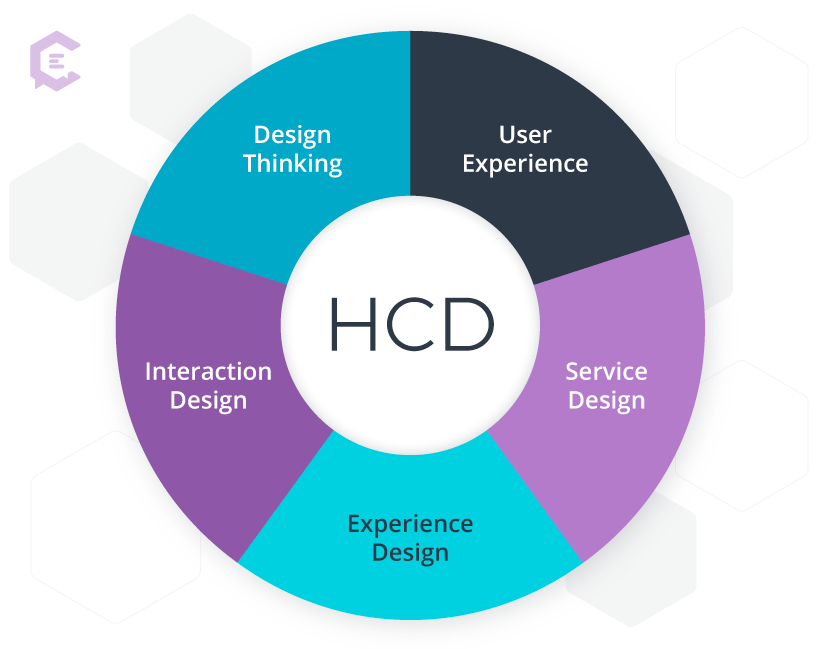
For those who are more visual, picture human-centered design as the hub of a wheel, with user experience, service design, experience design, interaction design, and design thinking as spokes on that wheel.
User experience, interaction design, and service design
In answering the question, “Is service design just customer experience, user experience or interaction design?” Polaine and his co-authors answer, “No. They are close cousins to service design, but they are not the same…Interaction and user experience design are often understood as design for screen-based interactions but service design covers a broader range of channels than this.”
Service design: principles, components, and parts
“Turn to service design when you’re looking at a customer experience that occurs over time with multiple touchpoints and you need to understand and address the details of that experience.” — Think Company
As we begin to dive deeper into service design with a content point of view, remember this: as with design thinking (and any other design-centric methodology), content (in its many forms) is a driver — or an integral component — of many products and services.
It’s difficult for customers and service providers to connect the proverbial dots without the right content at critical touchpoints to help reduce or eliminate friction or confusion. So even though we’ve been focusing on design as a discipline, content is very much a part of the service design approach. From this point on, we’ll be looking at the principles, components, and parts of service design through a more content-centric lens.
Service design principles
The Interaction Design Foundation refers to the following five principles of service design, first identified by This is Service Design Thinking authors Marc Stickdorn and Jakob Schneider:
- User-centered: Use qualitative research to design focusing on all users.
- Co-creative: Include all relevant stakeholders in the design process.
- Sequencing: Break a complex service into separate processes and user journey sections.
- Evidencing: Envision service experiences to make them tangible for users to understand and trust brands.
- Holistic: Design for all touchpoints throughout experiences, across networks of users and interactions.
As content creators, when we’re given the opportunity to establish an agreed-upon set of principles with our design partners at the start of a project, it helps foster the relationship by using a common language and ultimately helps to facilitate a collaborative process to ensure that there is useful content in support of every touchpoint identified as part of a service transaction.
Service design components
The Nielsen Norman Group identifies three main components of service design:
- People: Anyone who creates or uses the service, as well as individuals who may be indirectly affected by the service, including employees and customers.
- Props: Physical or digital artifacts (including products) that are needed to perform the service successfully, including physical spaces and digital environments.
- Processes: Workflows, procedures, or rituals performed by either the employee or the user throughout a service, including customer support, ordering products via an app for pick up, and so on.
Each of the components above involves content: people encounter content that helps them use a service; props, whether physical or digital, usually rely on signage or contextual help to facilitate wayfinding and securing the service needed; and processes are supported by content as well, such as the knowledge bases used by customer service representatives to render service, and microcopy in digital experiences that helps customers get the service they need.
Service design: a sum of parts
“Service design helps us visualize all the touchpoints and supporting activities to identify the real problems before focusing on a solution.” — Think Company
As we look at how to begin leveraging service design to find solutions to service problems — problems that are encountered by both consumers and service providers — we’ll first need to identify the parts of what the Interaction Design Foundation calls the service encounter:
- Actors: employees delivering the service
- Location: digital or physical environment where customers receive the service
- Props: objects used while delivering the service
- Associates: other organizations or teams involved in delivering the service
- Processes: workflows used to deliver the service
Here again, there are opportunities for content to play a role in service delivery, such as providing the information needed for employees to initiate the service workflows, or supporting information provided to associates to render the service.
Service design in action: the people and the process
As we move into implementing the work of service design, here are some questions that you’ll want to keep in mind:
- Who are the people involved?
- Which customers do you want to focus on?
- What are those customers trying to achieve?
- What is the company trying to achieve by offering the service?
The who: customers, employees, and stakeholders
Service design is all-inclusive: it considers every person involved in the service experience, including customers, employees, and stakeholders. As you begin the work of service design, you’ll want to identify people from each group to interview by way of questionnaires, surveys, or workshops.
The what: satisfactory service
Next in the process is to identify the service being sought after or offered. Here you’re seeking to understand the goal of the service from the standpoint of the customer and from the service provider, including the aforementioned employees and stakeholders.
This is the stage where you’ll begin to look at what’s happening before, during, and after the service experience, or as Think Company describes it, looking at a series of interactions that create experiences — the end-to-end journey — or how “all these interactions and activities work together to create one seamless experience.”
The how: service blueprint
As with most methodologies and frameworks, you’ll need a tool (or tools) to capture findings and map touchpoints on the service journey.
Enter the service blueprint.
“With a service blueprint, we can take a step back to look at the whole picture, and how everything works together before making changes.” — Think Company
In addition to capturing the processes or steps involved in securing a service, the Nielsen Norman Group notes that service blueprints also include:
Frontstage components:
- Channels
- Products
- Touchpoints
- Interfaces
Backstage components:
- Policies
- Technology
- Infrastructures
- Systems
This information can be captured during workshopping sessions with customers, employees, and stakeholders, on a physical whiteboard or virtually, like the example of a hospital service blueprint below from Miro.
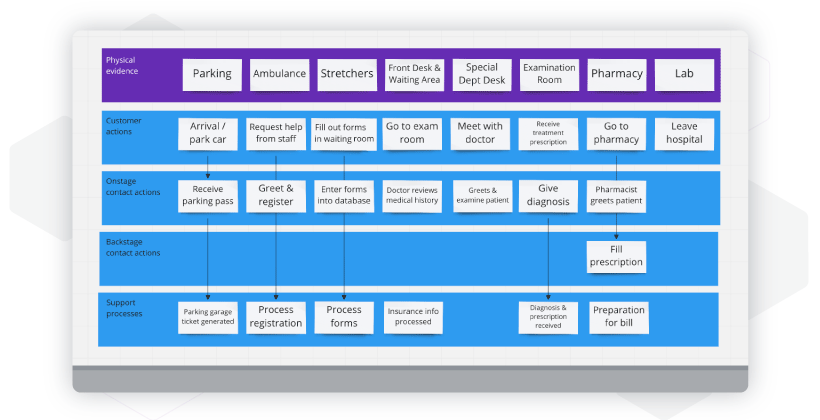
Start by listing the service process steps, plus frontstage and backstage components down the left side, from top to bottom. Then, working from left to right, use virtual or physical sticky notes or cards to capture the steps and components in a linear fashion.
For more complex services with multiple phases or stages, you may want to add swimlanes to group similar steps, as well as front- and backstage activities that happen along the way.
A service blueprint is a critical tool that will help you capture:
- Service goals
- Map touchpoints
- Customer emotions
As you move from the current state, the service blueprint will also help you identify service gaps that will reveal opportunities to make changes and solve problems that will help create change and move towards future state goals that support holistic service experiences.
Service design in action: the approaches, methods, and teams
Now that you know the who, what and how of service design, it’s time to put in the work. To be clear, the process is quite involved and requires adequate time and resources to make measurable change.
The Interaction Design Foundation lays out a comprehensive list of things to consider when doing service design, saying, “Remember to design for the complete experience. That means you should accommodate your users’/customers’ environment/s and the various barriers, motivations, and feelings they’ll have.”
Highlights from that list include:
- Understanding your brand’s purpose, the demand for it, and the ability of all associated service providers to deliver on promises.
- Prioritizing customer needs before the brand’s internal needs.
- Delivering unified and efficient services holistically — as opposed to taking a component-by-component approach.
- Including input from users.
- Streamlining work processes to maximize efficiency.
- Hosting co-creation sessions, which are vital to prototyping.
- Eliminating anything doesn’t add value for customers.
In Designing Services that Deliver, G. Lynn Shostack wrote, “A service blueprint allows a company to explore all the issues inherent in creating or managing a service.”
Some of those issues include:
- Identifying processes
- Isolating fail points
- Establishing time frames
- Analyzing profitability
According to Shostack, investing time and resources in service design activities, and specifically in creating a service blueprint, “…encourages creativity, preemptive problem solving, and controlled implementation. It can reduce the potential for failure and enhance management’s ability to think effectively about new services.”
By now it’s quite evident that it takes a village to do the work of service design. And while it might be easier to show how poor service delivery hurts the financial bottom line, it might be more difficult to make the case for securing the resources needed to do the work, especially if your team is already strapped for time, or doesn’t have the expertise to do the work.
There are agencies that specialize in this kind of work that you might consider. And another way to go is to make a pitch for teamlancing, either as a way to reinforce to members of your team who will be focused on carrying out the work of service design or to bring in teamlance talent that specializes in service design work and related activities.
The most important thing is that the work necessary to do service design — the research, the ideation, and the prototyping — gets done thoroughly and to completion. Bringing in teamlancers can help with that effort, and can help you succeed in improving service experiences for your customers and service providers.
Touchpoints: the intersection of content marketing and service design
“Content is a fundamental component of how users engage with a service, and content strategy is the mechanism that enables that service experience to be delivered holistically and consistently across all touchpoints.” — Jennifer McCutchen, Fjord
As the service and the accompanying customer journey is being mapped out and documented on the service design blueprint, content creators can and should be involved to ensure that clear and useful content is being mapped to those journeys. Again, this is where the gaps and opportunities are surfaced, and where content creators can add value to the process.

Content marketers who create branded content in support of services can look for opportunities to create marketing materials for a variety of channels to not only announce the availability of a service but to offer collateral that helps customers navigate the service being offered.
And digital content strategists and UX writers might identify existing content that is lacking or confusing — or worse yet, missing — that would help a customer seeking services through a digital interface.
No matter what label you identify with inside the content universe, the touchpoints identified in the service blueprint — and in fact, the entire service design process — are goldmines for those concerned with providing content that guides, instructs, and delights customers in need of services of any kind.
Or as McCutchen put it, “Illustrating how content is delivered on the frontstage but created and managed on the backstage, as well as how content can either strengthen or weaken the service experience, [helps to] drive home the symbiotic relationship between service design and content strategy.”
Go deeper: resource roundup
Perhaps you’re ready to take a deeper dive into service design, and you want to add more knowledge and methodologies to your toolbox. Or maybe your company has been tasked with figuring out a way to improve the service experience of your customers.
Luckily, there is no shortage of service design resources in the form of books, interactive tools, free resources, and more, with many available online. Here’s a bunch to get you started.
Books
- ‘This is Service Design Thinking‘
- ‘This is Service Design Doing‘
- ‘This is Service Design Methods‘
- ‘Service Design: From Insight to Implementation‘
Interactive tools
- Cuestellence Collaborative Journey Mapping Tool
- Miro Service Design Blueprint Guide
- Mural Digital Collaboration Tool
Free resources
- Nielsen Norman Group Service Blueprint Template
- This is Service Design Doing Method Library
- Service Design Tools
- Service Design Toolkit
Unlock your design power
People don’t always realize all the work that goes into design. It takes a creator with a specialized skill set and expertise to create graphics that attract and engage. We’ve curated a talent network of some of the best. If you’d rather harness the power of proven designers, connect with us here.