Duplicate content is a silent killer of a thriving website’s search engine rankings.
It’s not just problematic for search engines and your target audience. In some cases, duplicate content will also cause you confusion, especially when accidental content duplication happens.
Read this guide to learn what duplicate content is, why it occurs, how it affects SEO, and how to fix it.
Let’s begin.
What is duplicate content? SEO impact and considerations
Duplicate content is exactly what it sounds like — content that’s already published elsewhere.
Search engines like Google identify content via their web page URL. If the same content is published on two or more URLs, it’s flagged as duplicate content.
Contrary to popular belief, duplicate content isn’t a ground for a Google penalty — unless the duplicate content is widespread and determined as an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings.
Rather, duplicate content negatively impacts search engine rankings due to the following reasons:
- It confuses Google. Google can’t tell which copy of the content to index in search engine results. Rather than having one page with high rankings, you could have multiple pages with low rankings.
- Referring domains may point to the wrong URL. Backlinks are essential in increasing referral traffic and boosting overall rankings. With duplicate content, other websites may link to the wrong URL, causing you to miss out on the benefits of backlinks.
- It confuses readers. Duplicate content between different websites may confuse readers as to who published the original content. This can cost you recurring traffic and other SEO metrics tied to user engagement, like session duration and pages per session.
Duplicate content also has a negative impact on your brand.
Users might see your website as a hotbed of plagiarized content, making it difficult for them to trust you—let alone pay for anything your brand offers.
Duplicate content out of plagiarism also has legal repercussions. If the original creator/owner of plagiarized content proves that you used their material without proper citation or permission, you could face serious legal consequences.
How duplicate content is created
Avoid duplicate content pieces by understanding how they’re created in the first place.
1. Plagiarism
The biggest reason behind duplicate content is lazy writing. Some writers and sketchy content writing agencies engage in different levels of plagiarism, such as:
- Complete plagiarism: Using content scraping software (or straight-up copy-pasting content) to publish an article owned by someone else.
- Partial plagiarism: Copying a portion of an existing article, such as a paragraph or quote, and combining it with new content.
- Mosaic plagiarism: Paraphrasing sentences or using synonyms of words to make the content look original.
Other than these types of intentional plagiarism, there are also instances of accidental plagiarism. This involves unintentionally paraphrasing sentences or sections using a similar tone, angle, and group of words.
For example, if a writer conducts in-depth research and looks at existing blog posts, the original sources’ content may influence their write-up on a subconscious level. That’s why it’s important to include plagiarism checks in your content development workflow.
2. Template pages with filler text
Pages that use the same design template may get flagged for duplicate content due to filler text, like category page definitions, feature lists, and product descriptions.
This type of unintentional plagiarism commonly occurs in online stores. But they can also be present in poorly-structured, unoptimized, or incomplete business websites.
For example, a website may contain a template-based contact page with a bunch of pre-filled text. Without attention to detail, the website owner may leave duplicate information on the live page.
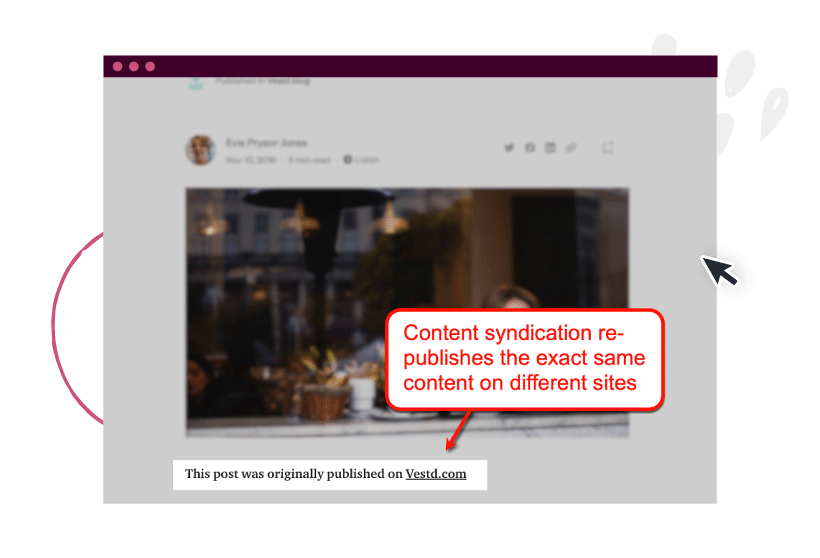
3. Content syndication
Content syndication is the process of re-publishing existing content on websites like Medium, LinkedIn, and Quora.
This is a legitimate way to spread your content and raise brand awareness. However, content syndication without proper link canonicalization can lead to duplicate content issues.
After all, the same piece of content is published on two websites.
Image Source: Medium.com
Without canonical links that tell Google which version is the original, rankings may be awarded to the syndicated copy rather than the actual post.
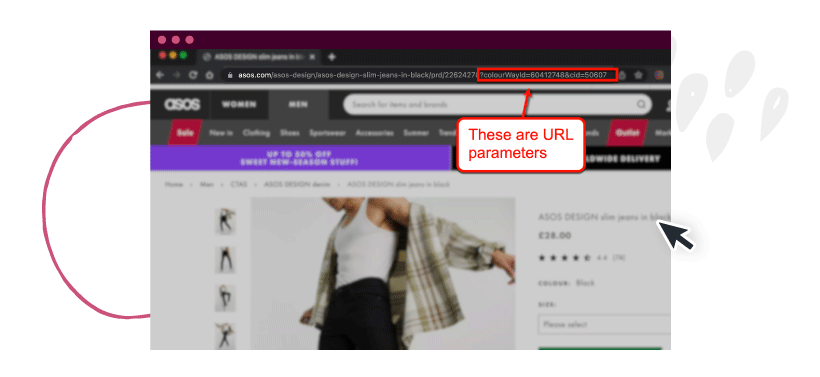
4. Additional URL parameters
URL parameters or “query strings” inject additional information into a URL.
These parameters are added after the question mark (?) symbol, and additional parameters are indicated by the ampersand (&) symbol.
URL parameters are often used in e-commerce websites. They’re primarily for sorting or filtering through product pages and categories, which can help users find the product variation they prefer.
Image Source: Asos.com
Automatically-generated URLs for different device types can also lead to duplicate content, like:
- https://www.example.com/blog/your-post
- https://m.example.com/blog/your-post
- https://amp.example.com/blog/your-post
Unfortunately, search engines see pages with URL parameters as entirely different pages with the exact same content. They target the same keywords, contain the same information, have the same links, and so on.
Use canonical tags to prevent these URL parameters from causing duplicate content issues.
How to fix duplicate content
So how do you fix the issue? You can prevent duplicate content problems from affecting your search rankings by taking the following steps:
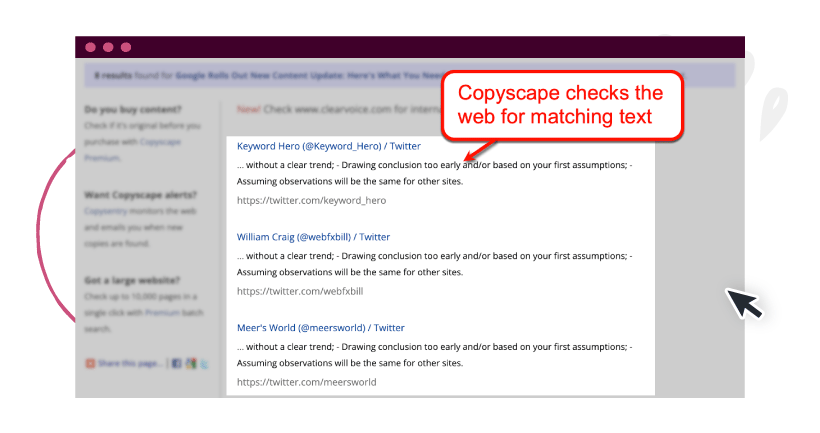
1. Use plagiarism checkers
Run your website content through tools like Copyscape to check for copies you may not know about.
Copyscape is a trusted platform that offers an on-demand plagiarism checking service.
They also offer a free option that checks the web for copies of already-published content.
Image Source: Copyscape.com
If you purchase content from an agency or outsource freelance writers, use Copyscape Premium to verify the originality of their draft before publishing it on your website. You can also use their Copysentry service to receive automatic alerts whenever copies of your website content are found on the internet.
2. Disable the copy command and right-click menu on your website
Protect your web content against plagiarists by disabling the copy command and right-click menu.
WordPress users simply need a plugin like WP Content Copy Protection & No Right Click to get this done. Otherwise, website owners may need to use CSS and JavaScript to disable these features manually.
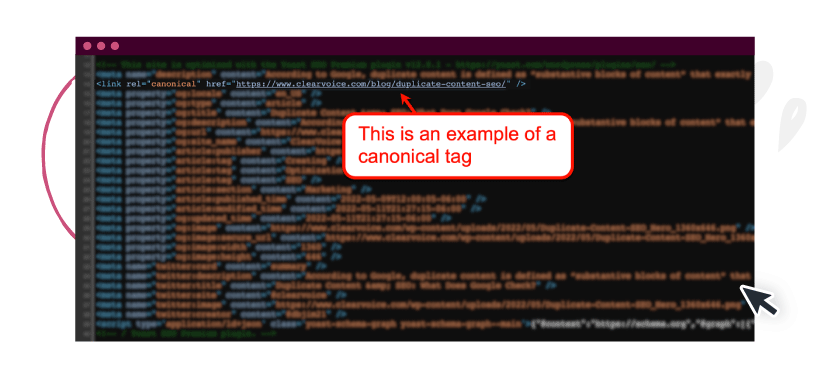
3. Use canonical tags
Specify the original content from a set of copies using the canonical tag.
To do this, simply add the “rel=canonical” tag to all duplicate pages you intentionally create. This tag should contain the link to the original content.
Canonical tags tell search engines where to look for the original source of duplicate content.
If you use content syndication services, make sure the publishing site also uses canonical tags.
4. Use a duplicate content checker or site audit tool
Internally check your website for existing duplicates using SEO audit tools.
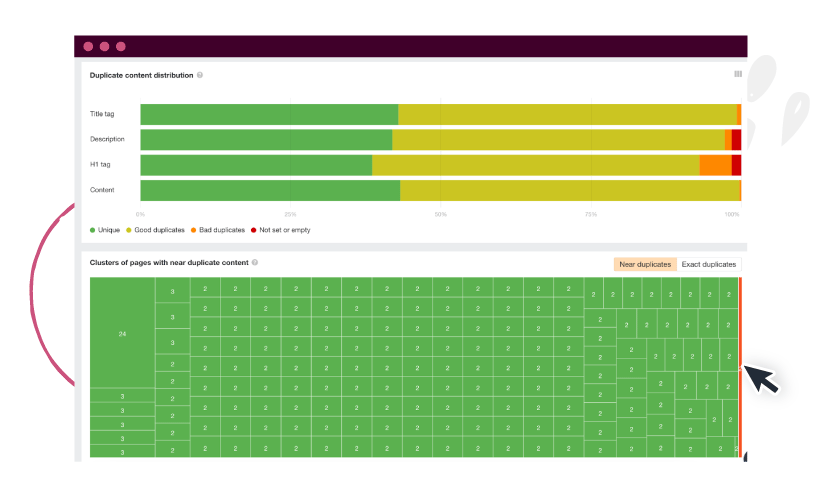
Ahrefs has a Site Audit tool that can check your website for “near duplicates” and “exact duplicates.”
Image Source: Ahrefs.com
If you find exact duplicates, use your discretion on whether to use link canonicalization or delete the copies outright. For near duplicates, especially those that only use similar headers, title tags, and meta descriptions, paraphrase or rewrite the problematic sections.
5. Use 301 redirects
A 301 redirect sends users from an old URL to the new, updated URL.
This is useful in domain migrations, which involve moving an entire website to a different address. It’s also helpful if you want to change or update permalinks of existing posts.
301 redirects can be done through your website’s .htaccess file, which is accessible from your hosting platform. For the exact steps, contact your web hosting service provider.
6. Hire vetted content experts
The best way to avoid duplicate content is to hire proven content writers who consistently deliver 100% original content.
Skilled content experts never resort to lazy writing tactics, like paraphrasing or article spinning. Their workflow may start with a borrowed idea, but they always create drafts from top to bottom using their own words.
Duplicate content: FAQs
How do I check for duplicate content?
If you’re worried about duplicate content with other websites, use plagiarism checkers like Copyscape. For internal duplicate content issues, run a site audit with a platform like Ahrefs.
Is duplicate content still bad for SEO?
Although duplicate content doesn’t directly affect rankings, it can affect the indexability of your original posts. Duplicate content can also affect the user experience and your brand image in a negative way.
What is the most common fix for duplicate content?
A 301 redirect is widely used for duplicate content created due to URL-related issues. If you need the old URL to stay live, use canonical tags instead.
Get original, top-quality content made by experts
Keep your website content helpful, top-notch, and 100% original by hiring the right content team for your business. Remember, your brand’s image and SEO are on the line wherever content is involved.
Talk to a content specialist today about your needs.