Duplicate content and SEO are a bad mix.
If you don’t want to run SEO campaigns that are downright apocalyptic, then you absolutely need to avoid duplicate content.
Instead, focus on creating pieces of content that are unique, value-packed, and optimized for the readers and the search engines.
To help you avoid the devastating effects of publishing duplicate content, we’ll take a deep dive into what duplicate content is, how it affects SEO, and what you can do to avoid it.
What is duplicate content in SEO?
The more you know about duplicate content and SEO, the easier it is to avoid any potential problems.
According to Google, duplicate content is defined as “substantive blocks of content” that exactly or partially matches content found elsewhere.
Duplicate content may be detected within the same website or published across various domains. Any website that publishes content may have duplicate content issues.
Whether the site owners have in-house writers or they work with third-party content contributors, in plenty of situations, websites unintentionally generate duplicate content though:
- Product and category pages: Some e-commerce websites use similar templates for products and category pages. These templates may contain chunks of the same information, such as category descriptions and checkout instructions.
- Staging sites: While rare, staging sites that lack the “noindex” tag for whatever reason can be considered duplicate content. Staging sites are experimental copies of websites used to preview and test new features and changes before going live.
- Pages with “printer” versions: Some websites create “printer-friendly” versions of pages for users who may want to take their research offline. While these versions are seen as duplicate content, they normally don’t have any negative effects on SEO.
- Generic website templates: New websites that never see heavy customizations may use templates for content management systems laden with pre-generated text. Some examples are WordPress-powered websites that use themes with default content for cookie-cutter pages, like contact pages, “About” pages, and so on.
- Multiple URLs that point to the same page: Google may detect duplicate pages for content that’s accessible with multiple URLs. For example, a landing page can be accessed using URLs with either HTTP or HTTPS as well as URLs with or without “www.”
These are some of the many examples where duplicate content is created unintentionally. Surprised at how easy it is to get duplicate content? The good news is that not all of them are bad.
Does Google impose a duplicate content penalty?
The short answer is yes — Google adjusts the ranking and indexation of sites that are found guilty of having duplicate content. However, this ONLY occurs if the content is deliberately copied to manipulate rankings or mislead users.
Certain types of duplicate content aren’t made with the intention of manipulating search rankings, like staging sites and product description copies.
Google already knows this, which is why they don’t automatically slap duplicate content penalties on every website that has them.
Why does Google care about duplicate content?
First, duplicate content can prevent the original posts/content from being credited with the rankings it deserves. And, in some cases, users may discover the same content appearing multiple times in search results.
This compromises the user experience and is unhealthy to the search engine as a whole.
Additionally, leaving duplicate content unchecked may lead to a surge of fraudulent or copycat websites that thrive by re-uploading existing content.
Keep in mind that users may perceive a website that copied several authoritative posts as trustworthy.
This essentially enables malicious actors to take advantage of the endless supply of online content to profit from shady practices—without investing in content creation themselves.
What types of duplicate content may lead to a Google penalty?
Worried about the possibility of duplicate content SEO penalties?
Statistically speaking, most website owners don’t have to think about it.
Duplicate content is surprisingly common. It’s actually a well-known fact that around 25-30% of the web is duplicate content.
But since a Google penalty can single-handedly kill a business online, one can never be too safe. Use Google Search Console to find out if you’ve received a penalty and follow the steps to mitigate it.
Here are the types of duplicate content that can have a negative impact on SEO:
1. Duplicate content made by content writers
Not all writers are created equal.
There are those who copy and paste content from other sites (cough—plagiarize—cough—so dangerous—cough).
While others endeavor to conduct extensive research and write masterfully to ensure they produce nothing but epic content.
That’s why you need to work with vetted freelance writers or teams.
By doing so, you collaborate with dedicated, professional writers that won’t copy and paste content from other sources.
What’s more, these are the types of writers who know how to write catchy titles, integrate conversion-inducing elements into their write-ups, and bring meaningful results to content marketing campaigns.
On the flip side, companies that end up publishing duplicate content due to their writers copying and pasting content face ginormous risks.
In addition to potential Google penalties, they could face lawsuits that could damage their reputation beyond repair.
2. Misconfigured syndicated content
Before anything else, it’s worth mentioning that content syndication is a legitimate marketing strategy that even pro marketers use.
Content syndication is the process of re-publishing an existing post to another website or platform. Some examples of content syndication websites include:
- Medium
- SlideShare
- Quora
Website owners deliberately use content syndication to reach a wider audience with their content. While it technically qualifies as duplicate content on different domains, it’s generally not a concern.
Unless the site that syndicated your content didn’t include a proper backlink.
Without a link, search engines wouldn’t know which version is the original. As a result, the syndicated content may end up outranking your site—if Google doesn’t hit you with a penalty first.
3. Scraped content
As a website grows in popularity, it may grapple with an increasing amount of duplicate content due to content scrapers.
In simple terms, content scrapers refer to software designed to bulk download content from websites — with or without the owner’s permission. It’s vastly different from other web scrapers that are only meant to extract specific data, like keywords and various metrics.
Black hat marketers use scrapers to steal content for various purposes, like spam and straight-up content theft. Whatever that purpose may be, illegal content scraping can result in duplicate content issues for the original source.
How can duplicate content be avoided?
Worried about duplicate content and SEO issues? The chances of Google penalties for duplicate content may be small, but they’re substantial.
Duplicate content may cause a website’s rankings to decline if Google detects malicious intent. In a few cases, a website gets blacklisted completely from appearing in search engine results.
Fortunately, there are several proven ways to avoid issues with duplicate content:
1. Syndicate with care
If content syndication is a crucial part of your content marketing strategy, do so with extra care.
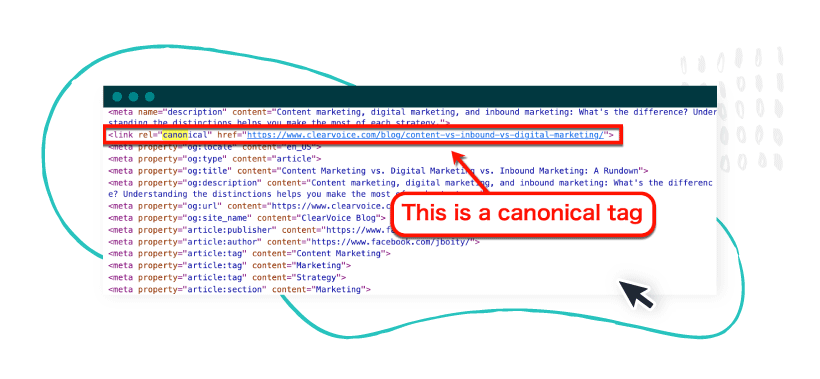
Make sure syndicated content contains a link with a “canonical” tag to the original content (also called a canonical URL).
Trusted content syndication websites do this by default. But for good measure, reach out and verify that there’s a canonical tag on each one of your articles.
Pro tip: use a duplicate content tool like Ahrefs to find duplicate content internally on your site or on different sites.
2. Use the “noindex” tag on archives and category pages
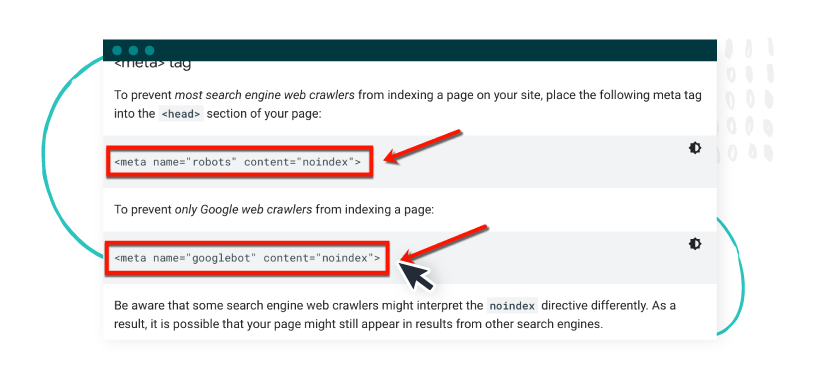
If Google is ranking archive or category pages over your content, you can block the indexing for those pages using the noindex tag.
All you have to do is paste a simple meta tag into your page or post’s “<head>” section.
To block all search engine crawlers from indexing a page, use:
- <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
If you only want to block Google from indexing a specific page, use:
- <meta name=”googlebot” content=”noindex”>
(Image Source: Developers.Google.com)
3. Check for bad duplicate content
There are dozens of tools out there that can automatically scan your website for bad duplicate content. A good example would be Ahrefs, which can check websites for bad duplicates through the Site Audit tool.
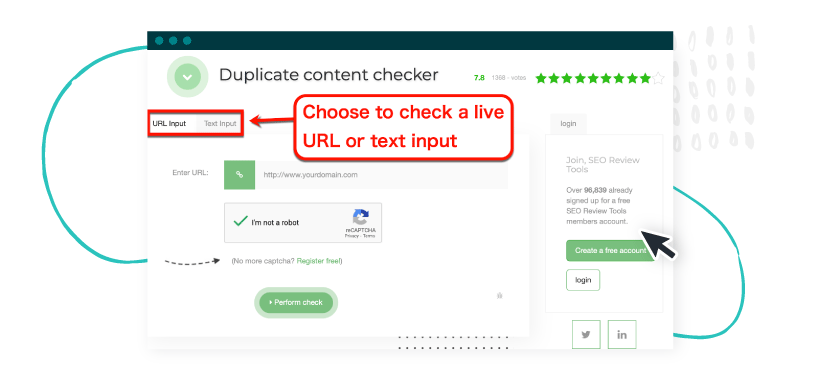
You can also use Duplicate Content Checker by SEO Review Tools to scan for internal and external duplicates on your website.
Image Source: SEOReviewTools.com
Internal duplicate content refers to repeated content within your website. External duplicates, on the other hand, refer to duplicate content on different sites.
Using tools makes it easy to spot unintentional duplicate content that can harm your website’s SEO profile.
If you find duplicate content, here are the things you can do to fix them:
- Designate the original content with a canonical tag
- Use the “noindex” tag on duplicates
- Remove the duplicate content
4. Use plagiarism checkers
For brands that source content from contractors, a tool like Copyscape guarantees you’re publishing 100% original content.
Copyscape is a time-tested plagiarism checker that can instantly check whether or not an article contains duplicate information. It is a must-have in every content marketing agency’s toolbox.
Image Source: Copyscape.com
Apart from on-demand plagiarism checks, Copyscape also features “Copysentry.” For as little as $4.95 per month, the tool will check the web for copies of up to 10 pages on a weekly basis.
Whenever someone steals your content and publishes it elsewhere, Copyscape will send an email alert for you to take action. You can ask to remove the duplicate content, request a canonical link, or file a DMCA takedown through Google’s Legal Help section.
5. Combine similar pages
Sometimes, pages that discuss the same topic contain similar information that may be seen as duplicates.
For example, you could have a listicle with overlapping items that have almost identical product descriptions. You may also have similar landing pages that target different cities, which may contain heaps of duplicate text.
In both scenarios, an easy fix is to consolidate information into one post.
Website owners should also avoid using generic page templates unless they plan to perform heavy customizations. This minimizes the chances of unintentionally creating duplicate content that can confuse readers as well as search engine crawlers.
6. Be consistent with internal links
When building internal links to specific pages, be sure to use the same URL each time.
Don’t link to “http://yoursite.com/blog/your-post/” in one article and “https://www.yoursite.com/blog/your-post/” in another. Using a single URL for multiple internal links signals that you’re linking to the canonical page.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does Google consider duplicate content?
Google defines duplicate content as blocks of content that contain information that’s similar or “appreciably similar” to existing content. Changing a few words with synonyms or even paraphrasing entire paragraphs isn’t enough to hide duplicate content from Google.
2. Is it okay to copy product descriptions?
Duplicate product descriptions don’t affect SEO in any way. As long as you’re not misleading readers, feel free to use copy-pasted product descriptions where they make sense.
3. What is the most common fix for duplicate content?
Using the rel=canonical tag fixes a lot of duplicate content issues, from dynamic URL parameters to content syndication. It’s a universal solution that tells Google how to find the original content.
Avoid duplicate content while dominating your industry
With the duplicate content and SEO tips above, you can avoid issues.
If you want a content marketing strategy free from duplicate content that can drive revenue and business growth, talk to a content specialist at ClearVoice today. Our team of seasoned producers, editors, and writers can handle all of your content needs.